




In recent years, India’s Over-the-Top (OTT) sector has witnessed exponential growth, transforming the way content is consumed across the nation. With the advent of affordable internet and the proliferation of smartphones, OTT platforms have become the go-to source for entertainment, news, and more. But Who Dominates India’s OTT Sector?
India’s OTT landscape is dominated by a few key players, each bringing something unique to the table. The most prominent platforms include Disney+ Hotstar, Amazon Prime Video, Netflix, and JioCinema. These platforms have carved out significant market shares by offering a diverse range of content tailored to the varied tastes of Indian audiences.
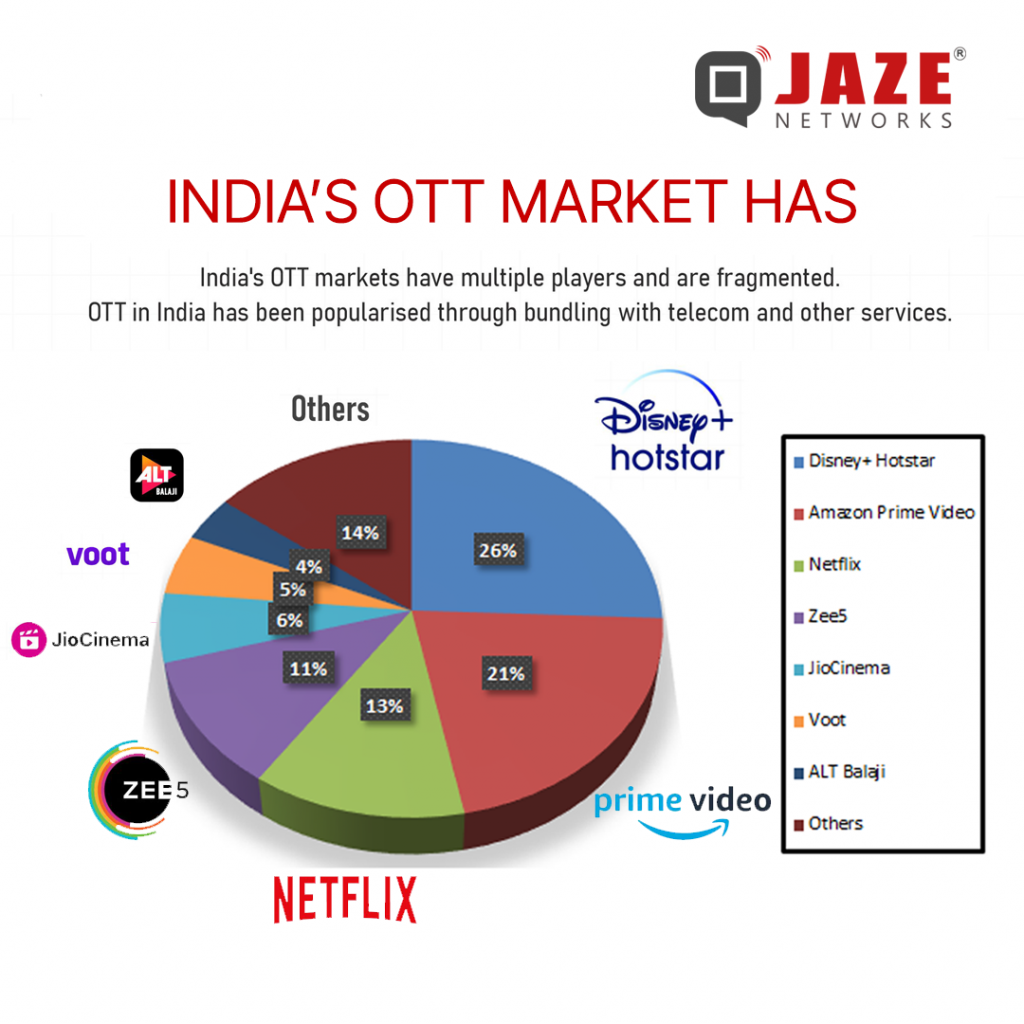
Disney+ Hotstar leads the pack with its extensive library of local and international content, including exclusive rights to stream major sports events like the Indian Premier League (IPL). This has made it a household name, especially among sports enthusiasts.
Amazon Prime Video follows closely, known for its vast collection of movies, TV shows, and original content. The platform’s investment in regional content has paid off, attracting a broad audience base across different linguistic demographics.
Netflix, while a global giant, has tailored its strategy to cater to Indian viewers by producing high-quality local content and acquiring rights to popular Bollywood films. Its focus on original series and movies has helped it gain a loyal subscriber base.
JioCinema, backed by Reliance Jio, leverages its extensive telecom network to offer affordable streaming services. Its integration with Jio’s telecom services provides a seamless experience for users, making it a strong contender in the market.
The Indian OTT market is characterized by its rapid growth and dynamic nature. As of 2024, the market is expected to exceed $10 billion, with over 500 million active users. This growth is driven by several factors:
Despite the optimistic outlook, the OTT sector faces challenges, including:
However, these challenges also present opportunities. The increasing demand for on-demand content and the integration of advanced technologies like AI and blockchain can help platforms differentiate themselves and offer unique value propositions to their users.
The future of India’s OTT sector looks promising. With the continuous rise in internet penetration and the growing preference for digital content, the market is poised for further expansion. Platforms that can innovate and adapt to the evolving preferences of Indian viewers will likely emerge as leaders in this space.
As the market continues to expand, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer behaviors, platforms that prioritize content diversity, user experience, and strategic partnerships are likely to maintain a competitive edge in this burgeoning industry.
Today all ISPs need to provide OTT services as a value add-on to retain subscribers and improve customer satisfaction. Jaze ISP manager integrates with all leading OTT platforms and OTT aggregators to automate billing for OTT services as well as activate and deactivate OTT services directly without manual intervention. Click here to learn more.
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a distributed group of servers spread across various geographic locations, working together to efficiently deliver Internet content. The primary role of a CDN is to enhance the speed, availability, and security of websites by serving content closer to the user.
CDNs are widely used to transfer web assets like HTML pages, JavaScript files, stylesheets, images, and videos. The growing reliance on CDN services means that a significant portion of today’s web traffic, including content from major platforms like Netflix, Amazon, and Facebook, is delivered via CDNs.
The key to a CDN’s functionality lies in its geographically distributed network of servers. Here’s a simplified overview of how a CDN works:
By distributing content in this way, CDNs are able to significantly enhance the performance and reliability of websites.
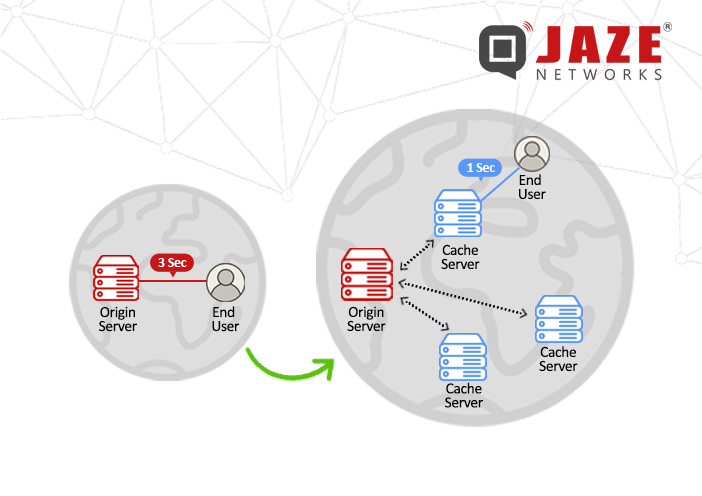
The advantages of using a CDN can vary depending on the size and needs of the website or application. However, the four primary benefits of a CDN are:
One of the biggest expenses for websites is the cost of bandwidth consumption for hosting. CDNs help reduce these costs by caching content, thereby reducing the load on the origin server. Since the CDN handles a significant portion of traffic, website owners can save on bandwidth expenses, making their operations more cost-efficient.
Websites often face the challenge of handling sudden spikes in traffic or dealing with hardware failures. A CDN, with its distributed infrastructure, can easily manage large volumes of traffic and better withstand hardware failures. This ensures that the website remains accessible even under heavy load, improving uptime and reliability.
Speed is a crucial factor for user experience. By serving content from servers that are closer to the end user, CDNs significantly reduce latency and enhance page load times. Faster loading websites are less likely to lose visitors due to slow performance, leading to reduced bounce rates and increased engagement. Studies show that users are more likely to leave a website if it takes too long to load, so CDNs play a vital role in improving visitor retention and satisfaction.
CDNs offer a range of security features, such as DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) mitigation, improved SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates, and other security optimizations. By distributing traffic across multiple servers, a CDN can help protect a website from DDoS attacks, where a server is overwhelmed by a flood of traffic. Additionally, by keeping malicious traffic away from the origin server, a CDN reduces the risk of cyberattacks and ensures that sensitive data is better protected.
CDNs play a vital role in the modern internet ecosystem by ensuring that web content is delivered quickly, reliably, and securely. Whether you’re running a small blog or a large e-commerce site, leveraging a CDN can provide significant benefits in terms of performance, cost savings, and security.
Most of the large CDN networks are available through peering at IXs. This helps ISPs who peer with them to significantly reduce bandwidth costs and deliver content faster. Jaze ISP Manager integrates with all leading BNGs which support multiple QoS policies to prioritize CDN traffic over other traffic streams. Click here to learn more
The landscape of entertainment consumption has dramatically transformed with the rise of video streaming, marking a significant shift from traditional broadcast TV to internet-based services.
As video streaming becomes increasingly popular, two key technologies have emerged: IPTV and OTT services.
According to recent data from Statista, the OTT video market is anticipated to reach approximately 6.4 billion users by 2029. Meanwhile, the global IPTV market was valued at USD 59.68 billion in 2022. But what are IPTV and OTT, and how do they differ?
Network Type: IPTV operates on a closed, managed network provided by Internet Service Providers (ISPs). This ensures a controlled environment for content delivery, leading to more stable and reliable streams.
OTT services utilize the open, public internet, making them accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
Monetization Models: IPTV services are typically subscription-based and often bundled with other internet services provided by ISPs.
OTT services offer more flexible monetization options, including both subscription-based and ad-supported models. This variety allows OTT platforms to cater to different user preferences and budgets, providing more accessibility and choice.
Content Quality: IPTV is known for delivering high-quality, reliable streams due to its controlled network conditions. The managed network minimizes buffering and interruptions, ensuring a smooth viewing experience.
OTT content quality, however, can vary significantly based on the viewer’s internet speed and network congestion.
Accessibility: IPTV services are limited to the service provider’s network, often making them region-specific. This means that users can only access IPTV content within the geographical area covered by their ISP.
OTT services are globally accessible as long as there is an internet connection. This global reach allows users to access content from anywhere in the world, making OTT a more versatile option for international viewers.
Equipment: To access IPTV services, users typically need a set-top box and sometimes additional hardware. This equipment is necessary to decode the IPTV signal and deliver it to the TV.
OTT services are accessible on a wide range of devices without the need for special equipment. Users can stream OTT content on smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and computers, providing greater convenience and flexibility.
Operational Costs: IPTV services incur higher operational costs due to the need for dedicated infrastructure and equipment. These costs are often passed on to consumers through higher subscription fees.
OTT services leverage existing internet infrastructure, resulting in lower operational costs.
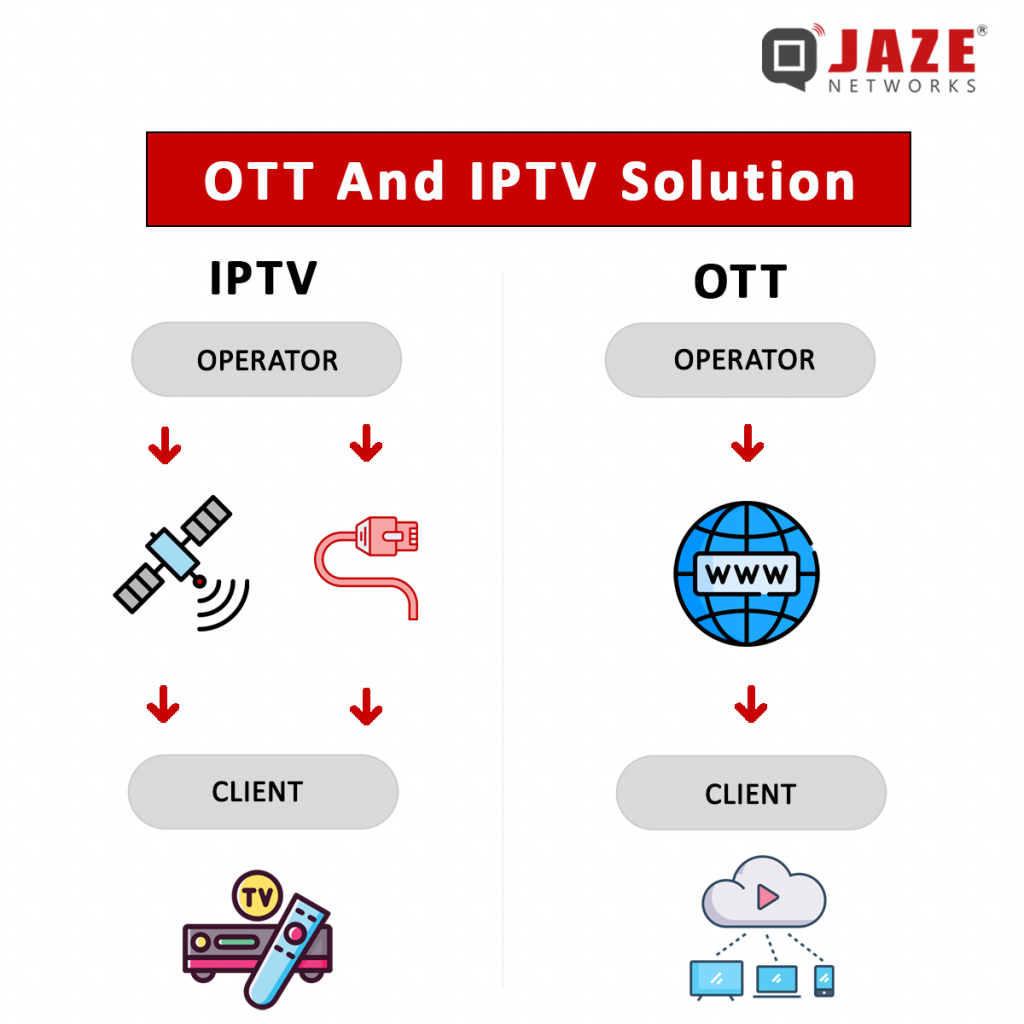
IPTV, or Internet Protocol Television, delivers television content through a private, managed network. This means that the service provider controls the entire delivery process, ensuring a high-quality, reliable viewing experience. IPTV typically requires a subscription and a set-top box to decode the signal and deliver it to your TV.
Once the setup is complete, users can enjoy a wide range of TV programming over their internet connection. In essence, IPTV represents a shift towards a more flexible and efficient television experience, offering on-demand access to a diverse array of programming through a managed network.
OTT, or Over-The-Top, refers to content delivered over the public internet. Unlike IPTV, OTT does not require a managed network or a set-top box. Instead, it can be accessed on a wide range of devices, including smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and computers. Popular OTT services include Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime Video.
While both IPTV and OTT offer unique advantages, OTT services have become the preferred choice for many consumers and providers. The flexibility and lower cost of OTT platforms make them more appealing, especially in today’s mobile-first world where users value the ability to watch content on-the-go.
OTT services also stand out for their user-friendly nature. There’s no need for specialized equipment or installation—just an internet connection and a device. This ease of use, combined with a vast library of on-demand content, has contributed to the widespread adoption of OTT over IPTV.
Choosing between IPTV and OTT depends on your specific needs and preferences. IPTV might be ideal for those seeking high-quality, live streaming within a controlled network, especially for events like sports. However, for most users, OTT offers a more versatile and cost-effective solution, allowing access to a broad array of content across multiple devices.
With ISPs offering multiple services, managing billing and services for OTT and IPTV can be challenging. Jaze ISP Manager simplifies this process by integrating with top OTT and IPTV platforms and aggregators. It automates billing and efficiently manages OTT and IPTV services, including activation and deactivation. Additionally, Jaze ISP Manager integrates with leading BNG providers to help deliver differentiated policies, enhancing the Quality of Experience for the ISP’s subscribers. Click here to learn more.