




When setting up a Wi-Fi network, you may have noticed two frequency options: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Both frequencies serve the purpose of providing wireless internet, but they operate differently, impacting speed, range, and interference. Let’s break down what each frequency offers to help you choose the best option for your needs.
The numbers 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz refer to radio frequency bands used to transmit data wirelessly. These bands enable devices like smartphones, computers, and smart home devices to communicate with a router, creating a Wi-Fi network. Each frequency has unique characteristics that can influence your connection’s strength and reliability.
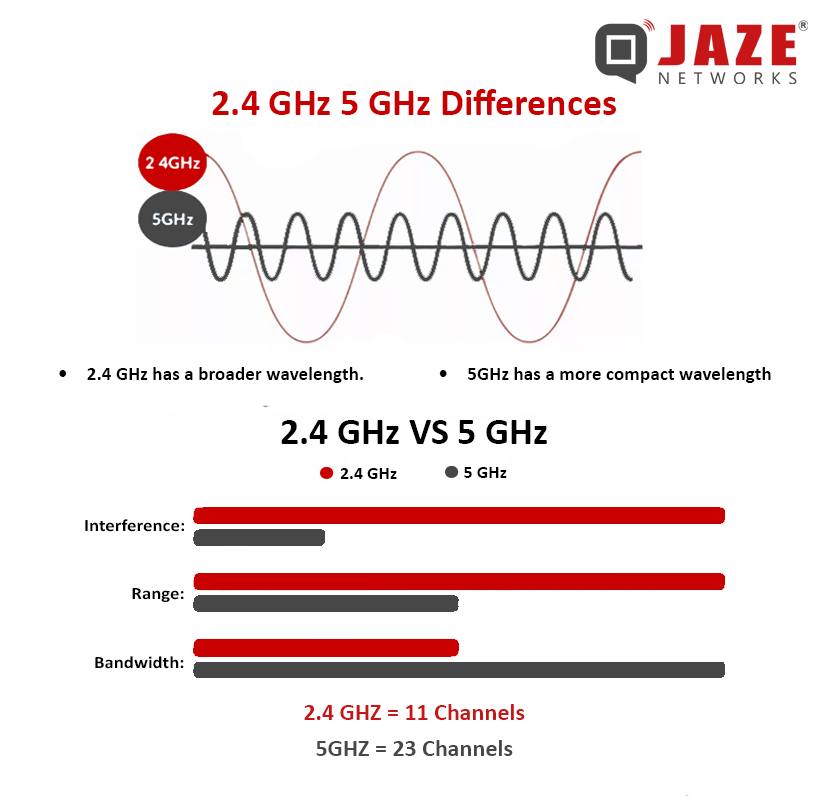
The 2.4 GHz band has been around for a while and is often considered the default frequency for most Wi-Fi devices.
Range: One of the main advantages of the 2.4 GHz band is its ability to cover longer distances. The lower frequency waves can penetrate walls and other obstacles more effectively, making it ideal for larger homes or office spaces.
Speed: While the 2.4 GHz band offers decent speeds, it generally maxes out at around 150 Mbps under ideal conditions. This might not be sufficient for data-heavy tasks like streaming HD videos or online gaming.
Interference: This band is more prone to interference because it shares the frequency with many other household devices, such as microwaves, cordless phones, and baby monitors. This can lead to slower speeds and dropped connections, especially in densely populated areas.
Compatibility: Most Wi-Fi devices support 2.4 GHz, making it a widely compatible choice.
The 5 GHz band is newer and offers several benefits, particularly in terms of speed and congestion:
Speed: One of the most significant advantages of the 5 GHz band is its ability to support higher data transfer rates. Speeds can reach up to 1,300 Mbps, making it perfect for activities that require a lot of bandwidth, such as streaming HD or 4K videos, online gaming, and large file downloads.
Interference: The 5 GHz band is less crowded compared to the 2.4 GHz band, resulting in less interference from other devices. This can lead to a more stable and faster connection, especially in environments with many Wi-Fi networks.
Range: The higher frequency of the 5 GHz band means it doesn’t cover as much distance as 2.4 GHz and struggles more with obstacles like walls and floors. This can limit its effectiveness in larger spaces or multi-story buildings.
Channels: The 5 GHz band offers more channels, which helps reduce congestion and improve performance in busy environments.
Choosing the right frequency band depends on your specific needs and environment:
2.4 GHz: Ideal for larger homes or offices where coverage over longer distances is crucial. It’s also better for penetrating walls and other obstacles. Use this band if you have older devices that only support 2.4 GHz.
5 GHz: Best for smaller areas or spaces with minimal obstacles where speed is a priority. It’s perfect for high-bandwidth activities like streaming and gaming. Use this band to reduce interference and improve connection stability.
Most modern routers are dual-band, meaning they can broadcast both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz signals simultaneously. This allows you to choose the best band for your needs or even connect different devices to different bands. For example, you could connect your smartphone and smart home devices to the 2.4 GHz band for better range, while using the 5 GHz band for your laptop and gaming console to ensure faster speeds and less interference.
Selecting between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi frequencies can significantly impact network performance, with each band offering unique benefits in range and speed. ISPs will need to choose between single band routers and dual band routers based on the customer’s bandwidth plan and home layout. These will play a crucial role to ensure optimal end user experience. Apart from this ISPs will also need to ensure that these devices are configured as needed and get visibility on devices connected to the Wi-Fi network.
Jaze ISP Manager has built-in ACS with support for TR069 to automatically provision the CPE device along with managing Wi-Fi settings. ISPs can also remotely troubleshoot Wi-Fi issues by gaining insights on connected Wi-Fi devices and signal strength directly from Jaze ISP Manager’s dashboard. Click here for more information. Click here to learn more.
Video codecs are essential in determining video quality, file size, and playback performance. H.264 and H.265 are two popular codecs, each offering unique benefits. Let’s explore their differences to help you choose the right one for your needs.
H.264, also known as Advanced Video Coding (AVC), is a widely adopted video compression standard used in a variety of applications, including streaming services, Blu-ray discs, and online platforms like YouTube. Its broad compatibility and efficiency have made it a favorite in the industry.
Key Features:
Compatibility: Supported across nearly all devices and platforms.
Compression Efficiency: Offers moderate compression with good video quality but produces larger file sizes compared to more recent codecs.
Lower Processing Power: Ideal for use on older devices due to its lower computing power requirements.
H.265, or High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), is the successor to H.264, developed to provide better compression while maintaining high video quality. It excels at high-resolution formats, like 4K and 8K, and significantly reduces file sizes without compromising visual quality.
Key Features:
Better Compression: Reduces file size by about 50% compared to H.264.
High-Resolution Support: Supports up to 8K resolution, making it suitable for modern content.
Adaptive Streaming: Ideal for smoother streaming at varying bandwidths.

H.265’s major advantage is its ability to maintain the same video quality as H.264 but at half the bitrate, which leads to significantly smaller file sizes. This is beneficial for streaming, storage, and reducing bandwidth usage.
| Feature | H.264 (AVC) | H.265 (HEVC) |
| Compression Efficiency | Good | Excellent |
| Compatibility | Very High | Moderate |
| Video Quality | High | Higher |
| Processing Power | Lower | Higher |
| Use Case | General use, live streaming, video conferencing | High-resolution content, storage-limited scenarios |
| Resolution | H.264/AVC Bandwidth Required | H.265/HEVC Bandwidth Required |
| 480p | 1.5 Mbps | 0.75 Mbps |
| 720p | 3 Mbps | 1.5 Mbps |
| 1080p | 6 Mbps | 3 Mbps |
| 4K | 32 Mbps | 15 Mbps |
Although H.265 offers superior compression, it requires more processing power for both encoding and decoding. This means that older devices might struggle to play H.265 videos unless they have dedicated hardware support for HEVC.
H.264: Works seamlessly on most older and modern devices.
H.265: May require newer hardware and HEVC support for smooth playback.
Use Cases
H.264: Ideal for live streaming, video conferencing, and platforms that require broad compatibility. It’s the go-to codec for general use and applications where reliability and universal support are crucial.
H.265: Best suited for applications requiring high-resolution video, such as 4K and 8K streaming, and situations where storage space is limited. H.265 is also a good choice for future-proofing content as more devices begin to support this codec.
Many modern platforms now support H.265/HEVC due to its enhanced efficiency for high-quality streaming. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) that allow H.265/HEVC ingestion from third-party encoders, include:
For ISPs seeking to optimize bandwidth delivery, Jaze ISP Manager seamlessly integrates with top BNG providers supporting both RADIUS and Diameter protocols for flexible policy delivery and ensuring a seamless end user experience. Click here for more information.
As the landscape of home entertainment evolves, the competition between IPTV (Internet Protocol Television) and traditional cable TV intensifies. With the growing trend of cord-cutting, viewers face a pivotal decision about which option aligns best with their viewing preferences and lifestyle. This guide examines the essential differences between IPTV and cable TV, empowering you to make an informed choice about your entertainment future.

Cable TV: The Traditional Approach
Cable TV has long been the dominant method for delivering television content. It relies on coaxial cables to transmit signals to your TV. This well-established technology provides some clear benefits:
Stability: Cable TV is reliable and less dependent on external factors like internet speed.
Quality: Picture and sound quality remain consistent without buffering issues.
However, cable TV does come with its limitations. It is geographically bound, meaning you need access to the provider’s physical network, and the channel selection is often bundled into large packages, which may include unwanted content.
IPTV: The Internet Revolution
IPTV is a modern alternative, utilizing your internet connection to stream content. It offers significant flexibility in terms of device compatibility, letting you watch on your TV, smartphone, or tablet. With IPTV, users enjoy:
Customization: Pick the channels or programs that interest you, instead of settling for bundled packages.
Global Access: View content from around the world, bypassing geographic limitations.
Cable TV: Bundled Services and Contracts
Cable TV providers often offer bundled services that include internet and phone packages. While this might seem cost-effective at first glance, hidden fees for equipment rentals or installation, along with long-term contracts, can make it more expensive in the long run.
IPTV: Flexible and Transparent Pricing
IPTV services usually have straightforward pricing models. With subscription-based plans, you can pay for just the content you want, without any long-term commitment. Additionally, there are no equipment rentals or hefty installation fees, which makes IPTV an attractive option for those seeking flexibility in budgeting.
Cable TV: Familiar Offerings
Cable TV provides access to a wide range of channels, including local programming and live sports. However, its content library is often restricted to what the provider offers within its region, limiting options for international or niche programming.
IPTV: A World of Content
One of IPTV’s major advantages is its vast library of on-demand content, spanning across different genres, languages, and countries. IPTV platforms allow you to explore international programming and tailor your viewing experience based on specific interests, whether it’s niche content or blockbuster movies.
Cable TV: Traditional Navigation
Cable TV interfaces are generally simple but dated. Users navigate through a traditional TV guide, and DVR options allow for recording shows. However, searching for specific content can be slow, and the interface is not designed for personalized recommendations.
IPTV: Modern and Intuitive
IPTV services often provide more user-friendly platforms. You can search for content quickly, receive personalized recommendations based on viewing history, and synchronize your watching experience across multiple devices. This modern convenience is a big win for users who want an effortless interface.
Cable TV: Consistent Performance
Cable TV offers stable picture quality, with many channels available in high definition (HD). However, 4K content is still rare in traditional cable packages, limiting options for viewers with ultra-high-definition TVs.
IPTV: Leading the Quality Race
IPTV is more advanced when it comes to high-quality content. Many services provide access to 4K resolution and HDR (High Dynamic Range) content. Additionally, IPTV platforms use adaptive streaming, adjusting picture quality based on your internet speed, ensuring a smooth viewing experience.
Cable TV: Stability Under All Conditions
One of the major advantages of cable TV is its reliability. It remains unaffected by internet outages, and performance is generally consistent. It’s less susceptible to external factors like weather, making it a dependable choice.
IPTV: Dependent on Internet Connectivity
IPTV services, however, depend entirely on your internet connection. This means that buffering, reduced quality, or even service interruptions can occur during periods of slow or unstable internet. High-speed broadband is essential to ensure a smooth viewing experience.
Cable TV: Regulated and Secure
Cable TV is governed by strict regulations, ensuring all content is licensed and distributed legally. There’s also less concern over data collection, as cable TV providers don’t typically track or sell your viewing data.
IPTV: A Mixed Legal Landscape
While many IPTV providers operate legally, some services can fall into legal gray areas, particularly if they offer content without proper licensing. Users should be cautious and opt for reputable IPTV providers that comply with local regulations. Additionally, some IPTV services may collect and share user data, so reviewing privacy policies is essential.
Choosing between IPTV and cable TV comes down to your priorities. If stability and reliability are your main concerns, cable TV remains a solid option. On the other hand, if you’re looking for flexibility, customization, and access to a wider range of content, IPTV is the way forward.
Jaze ISP Manager seamlessly integrates with all major IPTV, OTT platforms, and OTT aggregators, offering a fully automated solution for managing video services. Combined with Jaze’s powerful support for high-concurrency RADIUS and DIAMETER services, ISPs can efficiently manage both bandwidth and entertainment needs for triple play service, ensuring a seamless end-user experience. Click here to learn more.