




A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a distributed group of servers spread across various geographic locations, working together to efficiently deliver Internet content. The primary role of a CDN is to enhance the speed, availability, and security of websites by serving content closer to the user.
CDNs are widely used to transfer web assets like HTML pages, JavaScript files, stylesheets, images, and videos. The growing reliance on CDN services means that a significant portion of today’s web traffic, including content from major platforms like Netflix, Amazon, and Facebook, is delivered via CDNs.
The key to a CDN’s functionality lies in its geographically distributed network of servers. Here’s a simplified overview of how a CDN works:
By distributing content in this way, CDNs are able to significantly enhance the performance and reliability of websites.
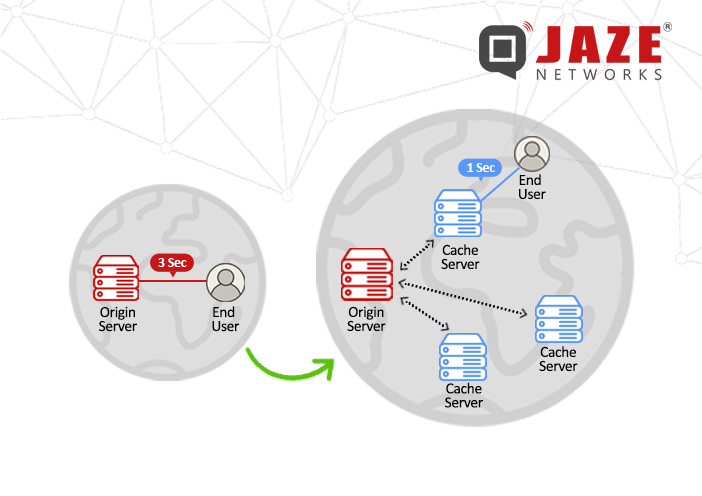
The advantages of using a CDN can vary depending on the size and needs of the website or application. However, the four primary benefits of a CDN are:
One of the biggest expenses for websites is the cost of bandwidth consumption for hosting. CDNs help reduce these costs by caching content, thereby reducing the load on the origin server. Since the CDN handles a significant portion of traffic, website owners can save on bandwidth expenses, making their operations more cost-efficient.
Websites often face the challenge of handling sudden spikes in traffic or dealing with hardware failures. A CDN, with its distributed infrastructure, can easily manage large volumes of traffic and better withstand hardware failures. This ensures that the website remains accessible even under heavy load, improving uptime and reliability.
Speed is a crucial factor for user experience. By serving content from servers that are closer to the end user, CDNs significantly reduce latency and enhance page load times. Faster loading websites are less likely to lose visitors due to slow performance, leading to reduced bounce rates and increased engagement. Studies show that users are more likely to leave a website if it takes too long to load, so CDNs play a vital role in improving visitor retention and satisfaction.
CDNs offer a range of security features, such as DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) mitigation, improved SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) certificates, and other security optimizations. By distributing traffic across multiple servers, a CDN can help protect a website from DDoS attacks, where a server is overwhelmed by a flood of traffic. Additionally, by keeping malicious traffic away from the origin server, a CDN reduces the risk of cyberattacks and ensures that sensitive data is better protected.
CDNs play a vital role in the modern internet ecosystem by ensuring that web content is delivered quickly, reliably, and securely. Whether you’re running a small blog or a large e-commerce site, leveraging a CDN can provide significant benefits in terms of performance, cost savings, and security.
Most of the large CDN networks are available through peering at IXs. This helps ISPs who peer with them to significantly reduce bandwidth costs and deliver content faster. Jaze ISP Manager integrates with all leading BNGs which support multiple QoS policies to prioritize CDN traffic over other traffic streams. Click here to learn more
Imagine returning home after a long workday to find everything prepared for you—a cup of tea and dinner ready just as you like it. While this may seem fantastical, futurologist Ray Hammond predicts such scenarios could become reality by 2040.
The Emergence of Smart Homes
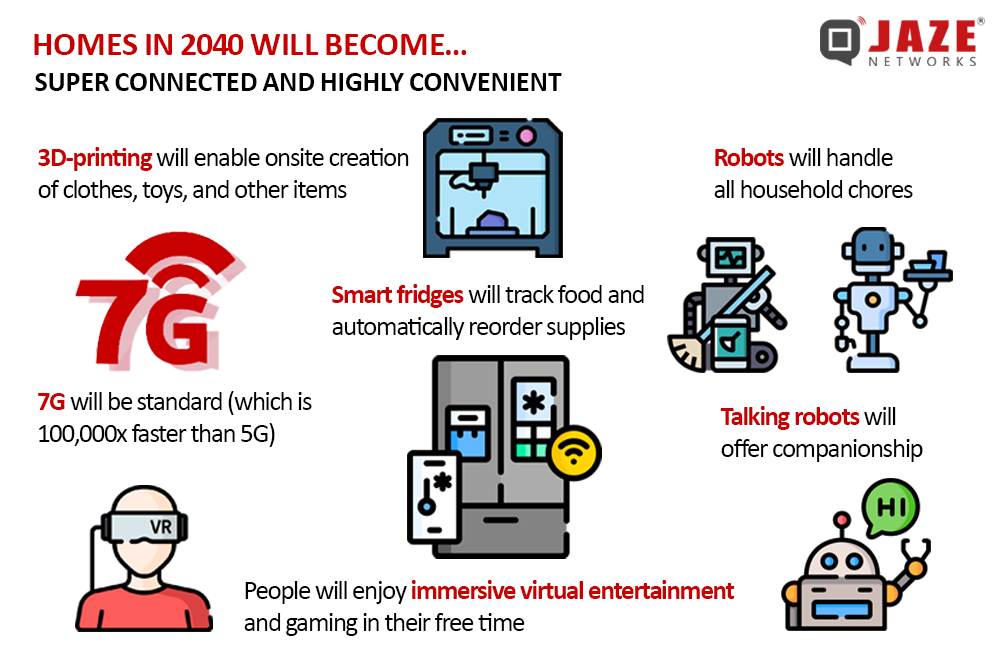
In the coming two decades, technological advancements have the potential to transform our living environments into self-sustaining ecosystems. Consider the prospect of homes constructed using 3D printing technology, with robotic workers assembling the components. This innovation could result in a substantial reduction in construction costs—potentially by as much as 60%—and timelines, allowing for new residences to be move-in ready in as little as two weeks. Equipped with smart sensors, these homes will intuitively respond to the needs of their occupants, fundamentally altering our interactions with our living spaces.
The Advent of 7G Connectivity
By 2040, the introduction of 7G technology may provide internet speeds up to 100,000 times faster than current 5G networks. Such advancements would enable the creation of immersive virtual reality experiences that blur the lines between digital and physical realities, transforming the ways we socialize, learn, and entertain ourselves.
Security in a Digital Fortress
The inconvenience of misplaced keys may become a relic of the past, as homes of the future will be secured through sophisticated facial recognition systems capable of identifying not only humans but also pets. Homeowners will have the capability to monitor their residences remotely, ensuring security even in their absence. Furthermore, continuous updates from maintenance sensors will detect potential hazards before they escalate, thereby enhancing the safety of these digitally fortified environments.
Achieving Energy Independence
Future residences are anticipated to utilize 75% less energy and to implement efficient water recycling practices. Innovations in solar technology will replace traditional bulky panels with aesthetically pleasing windows that also produce power. This move toward energy independence is vital as we strive for sustainable living solutions.
An Interactive Experience
The homes of the future will serve as responsive environments, equipped with voice recognition technology to facilitate commands for temperature adjustments, meal preparation, and more. Robotic assistants will manage household tasks, oversee grocery orders, and maintain gardens. Cooking will become increasingly effortless, as smart appliances prepare meals according to pre-programmed recipes.
Evolving Shopping and Entertainment
The potential of 3D printing may extend beyond housing to encompass clothing and household items, thus streamlining the shopping experience. Additionally, entertainment will evolve to be more interactive, integrating virtual and augmented reality. This may allow individuals to engage with holographic representations of historical figures or partake in immersive experiences that stimulate all five senses.
While the vision of future homes is intriguing, it prompts critical questions regarding the pace at which we can transition to this digital future. Factors such as technological innovation, economic conditions, and societal acceptance will play significant roles in shaping our living environments.
In the future, more devices will be connected to the Internet than ever before. Each device will require a unique IPv6 address, as the IPv4 pool is nearly exhausted. Service providers will need to roll out services exclusively on IPv6 to accommodate the increased number of connected devices. Adopting IPv6 today will ensure a smooth transition to handle the growing number of IoT devices in the future.
Jaze ISP Manager helps ISPs deploy IPv6 services on their networks, integrating with leading BNG providers to be future-ready for IoT. By eliminating the traditional NAT with IPv4, it ensures seamless Internet connectivity. Click here to learn more.
As digital consumption continues to rise, bandwidth management has become crucial for businesses, especially those reliant on cloud services. Bandwidth, the amount of data transferred over a network in a given time, plays a significant role in determining operational costs. Without effective control, bandwidth expenses can escalate quickly, particularly in industries dependent on high volumes of data transfer.
This article will explore the key factors influencing bandwidth costs and provide strategies to reduce them.
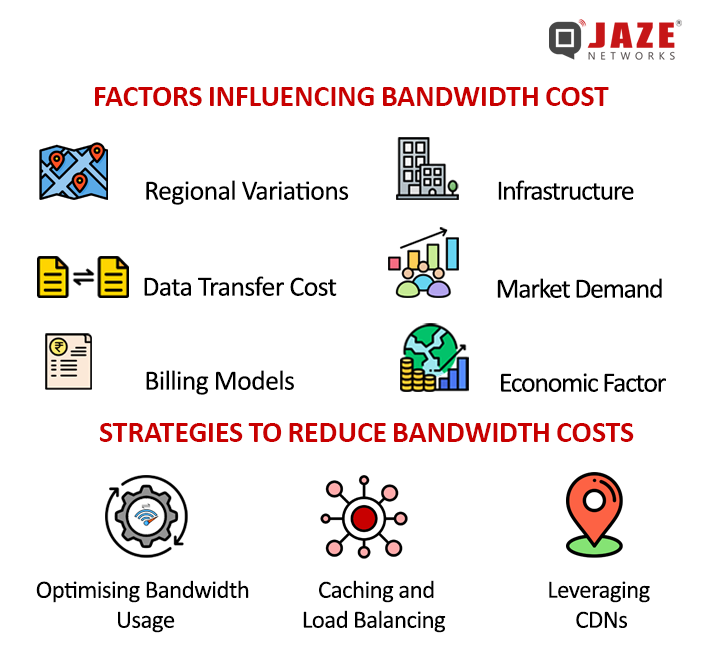
Factors Influencing Bandwidth Costs
Understanding what drives bandwidth expenses helps businesses manage their usage efficiently and avoid unnecessary costs. Here are some critical factors that affect bandwidth pricing:
1. Regional Variations
Bandwidth costs can differ based on geographic regions. Areas with advanced infrastructure and competitive markets tend to have lower costs. Conversely, regions with underdeveloped infrastructure or monopolistic market conditions face higher prices.
2. Data Transfer Costs
Many providers charge based on the volume of data transferred, typically measured in gigabytes (GB). Outbound data (sent from your network) often incurs higher costs compared to inbound data (received by your network). Providers like Google Cloud or AWS follow this model, where inbound transfers may be free, but outbound data can significantly drive up costs.
3. Billing Models
Different billing models can influence how much you pay for bandwidth:
Flat-Rate Pricing: A fixed monthly fee ensures cost predictability but may result in paying for unused bandwidth.
Pay-As-You-Go: Costs are based on actual usage, which is flexible but can lead to high expenses during peak periods.
Tiered Pricing: A tier-based approach offers a balance of predictability and flexibility, accommodating business growth.
4. Infrastructure and Peering
Regions with well-developed peering exchanges enable more efficient data transfer between networks. This reduces bandwidth costs by lowering the need for long-distance data transmission.
5. Economic Factors
Bandwidth costs are also affected by external factors such as power, cooling, and real estate costs. Data centers located in regions with high electricity prices or expensive real estate tend to pass those costs onto their customers.
6. Market Demand
In areas of high internet demand, especially during peak times, service providers may increase prices. High market demand for bandwidth can drive up prices, particularly in growing internet markets.
Strategies to Reduce Bandwidth Costs
To manage bandwidth expenses effectively, businesses must adopt strategies that optimize their data usage. Here are some key ways to reduce bandwidth costs:
1. Optimizing Bandwidth Usage
Managing bandwidth usage is essential for minimizing unnecessary data transfer:
Data Management: Prioritize essential data transfers and schedule non-essential ones during off-peak hours to reduce congestion.
Compression Techniques: Compressing large files such as images or videos before transferring them can drastically reduce the amount of data sent, lowering bandwidth costs.
Monitor Usage: Regularly analyzing bandwidth usage can reveal inefficiencies or heavy usage patterns, guiding businesses to implement specific cost-saving measures.
2. Caching and Load Balancing
Caching allows frequently accessed data to be stored locally, reducing repeated data transfers. For instance, implementing caching for images or videos can drastically cut data transfer to and from the server. Load balancing helps distribute network traffic across multiple servers, reducing the strain on any single server and preventing bandwidth overuse.
3. Using Content Delivery Networks (CDNs)
A CDN consists of a network of servers distributed across multiple locations, which cache and deliver content closer to users. CDNs reduce the load on the original server by handling static content like images, CSS files, and videos. This minimizes the need for repeated data transfer from the origin server, leading to significant bandwidth savings. CDNs are highly effective, often managing 60-80% of a website’s bandwidth, allowing the original server to focus on more critical functions.
Monitoring bandwidth usage regularly will also help businesses avoid unexpected costs and ensure more efficient network management. Implementing these methods can provide both immediate savings and long-term benefits, making them crucial for growing companies in today’s digital landscape.
Jaze ISP Manager provides comprehensive tools for monitoring bandwidth usage, offering real-time insights and detailed usage reports. This solution enables Internet Service Providers (ISPs) to manage end-to-end operations, including subscriber lifecycle management, billing, and policy enforcement. With features like automated provisioning, flexible billing options, and integration with various network equipment, Jaze ISP Manager helps businesses optimize resource allocation and ensure efficient network performance. Click here to learn more